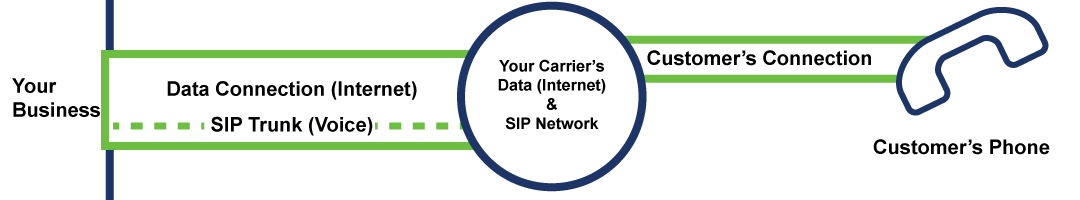
Since the PSTN’s main purpose is to handle voice connections, there is always a guaranteed bandwidth capacity and availability for phone calls. Voice calls through the PSTN will always take priority over any other type of potential traffic. Likewise, PRI Circuits always have a guaranteed amount of bandwidth set aside for each call that can never be used for anything else. SIP Trunking, however, cannot always guarantee this QoS. Since each voice connection is sent as a packet like any other piece of data, it is subject to lag, delay, high pings, or packet loss. These are not usually issues for websites or emails, since the server will continue sending the same packet repeatedly until your computer receives it. However, with the real time transmission of Voice, these packets can typically only be sent once. If the packet doesn’t make it, it may sound a lot like when someone is on their cell phone with poor coverage. Currently the only way to provide a QoS for a SIP Trunk is to purchase an MPLS, and the circuit from the same provider offering the SIP Trunk. Since you’re using the same carrier for all of the services, they can prioritize the voice packets for you.